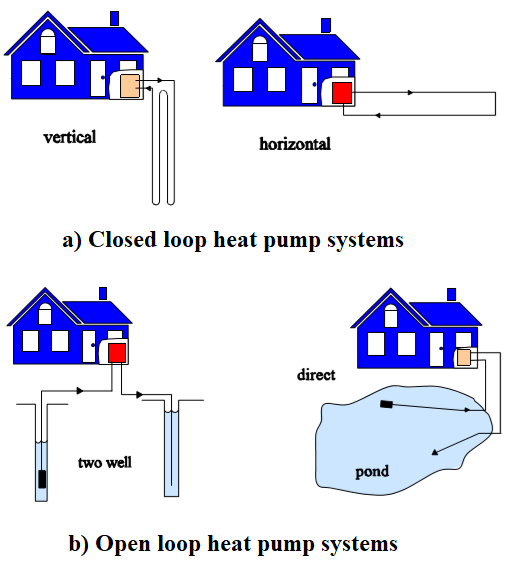
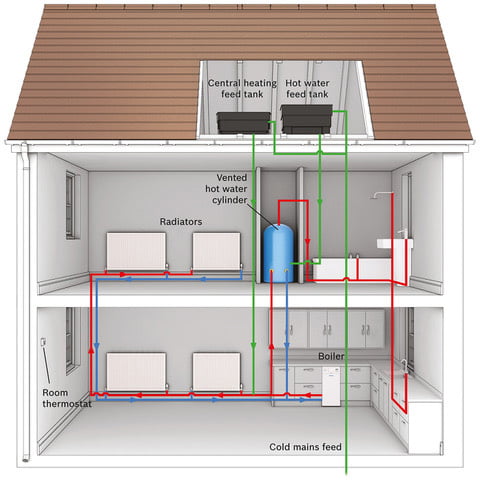
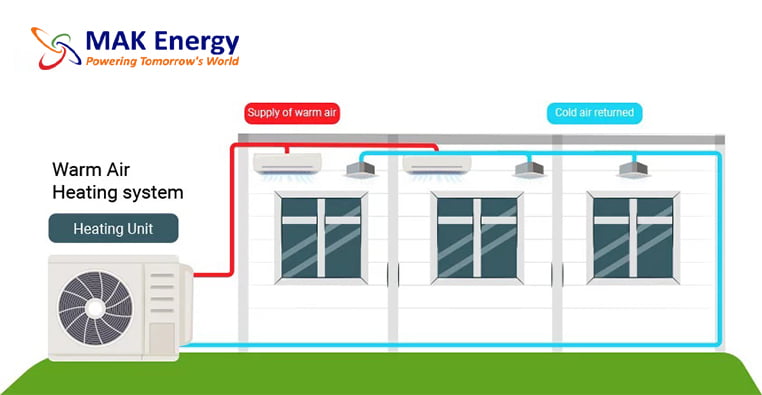
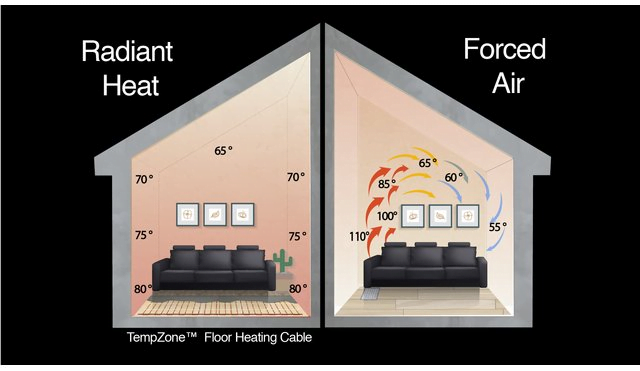
An air source heat pump represents an environmentally friendly, cost-effective, and low-carbon method of heating homes. This system delivers enough heat throughout the year at highly economical rates. Furthermore, if you’re eligible for government incentives to support the installation, it transforms into an even more appealing investment.
As the government focuses on installing an air source heat pump and energy-efficient renewable systems and phasing out traditional methods of heating homes and commercial buildings, such as gas boilers, air source heat pumps have become increasingly sought after. This trend is expected to persist for future generations.

In this blog, we will discuss the complete process of air source heat pump installation. The task is complex and requires a significant amount of engineering expertise and professional knowledge to ensure proper installation, maximizing efficiency and reliability. There are three main steps involved in the installation of an air source heat pump:
- Pre-Installation: This step includes conducting a survey and assessing the accessibility of the installation site.
- Installation Process: This stage encompasses installing air source heat pump indoor and outdoor units and establishing the necessary connections between them.
- Post-Installation: This phase involves verifying the functionality of the system and outlining the required maintenance procedures.
No matter, how complicated the process is, MAK Energy has the experience of handling air source heat pump installation. Reach out to MAK Energy for your air source heat pump installation and get the free no obligation quote and complimentary online survey by just filling out our quotation form which takes no more than a minute.
Important Note: What is EPC?
Before reaching out to the installer, you may need an Energy Performance Certificate. This certificate is particularly obtained when customers plan to apply for a grant. The EPC assesses your home’s energy efficiency and rates it from A to G, where A signifies high efficiency and G indicates low efficiency. By obtaining an EPC, you will also be able to estimate the expected heating costs for your home.
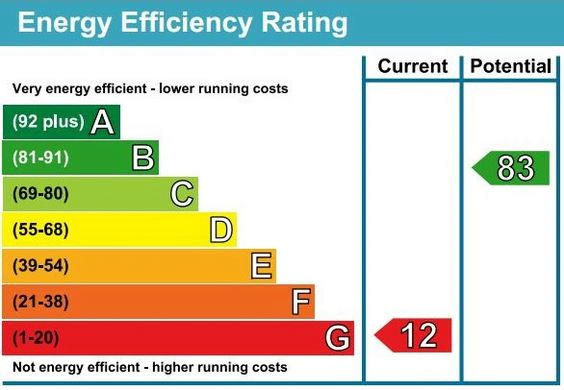
After obtaining the EPC, you can get in touch with the installer for a quotation. MAK Energy is always available to provide you with a quote for an efficient heating system.
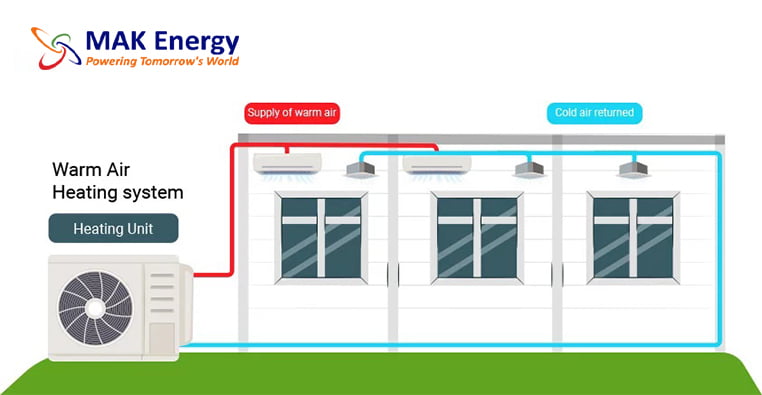
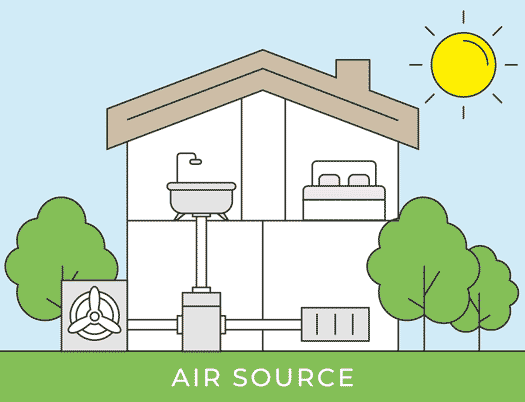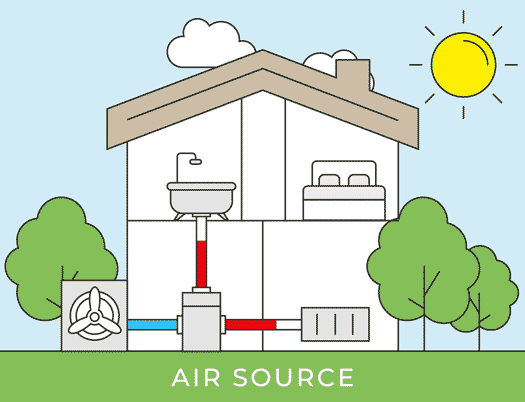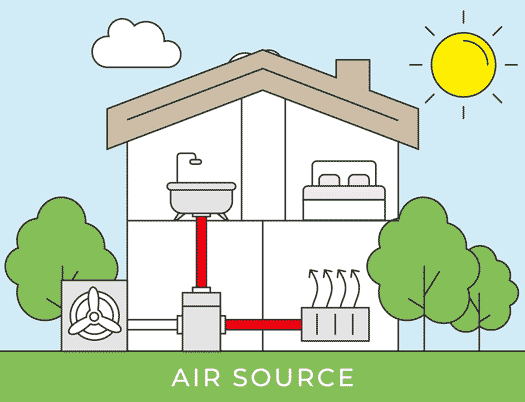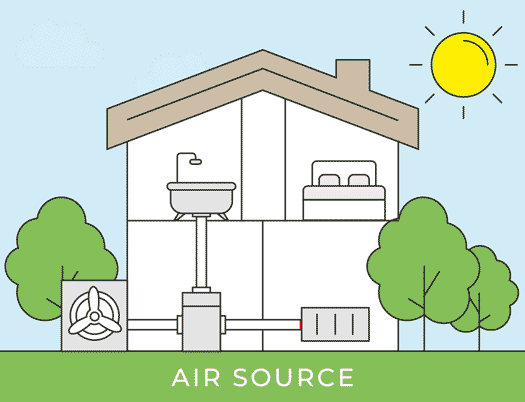
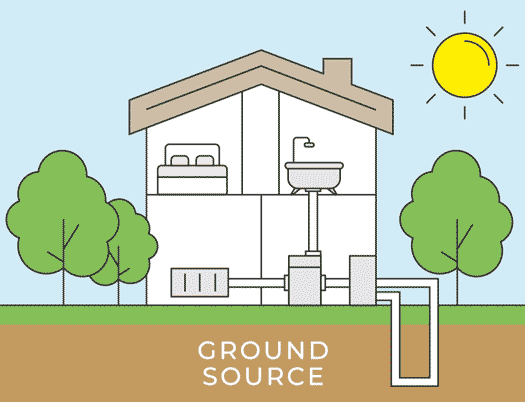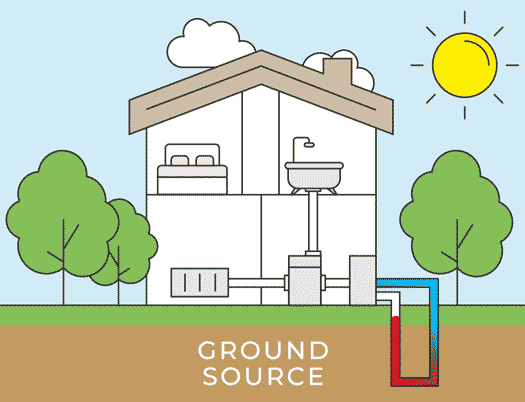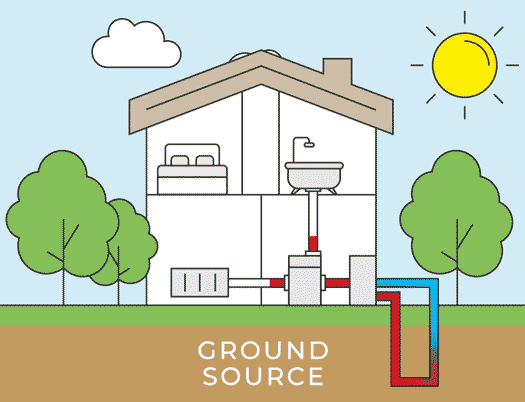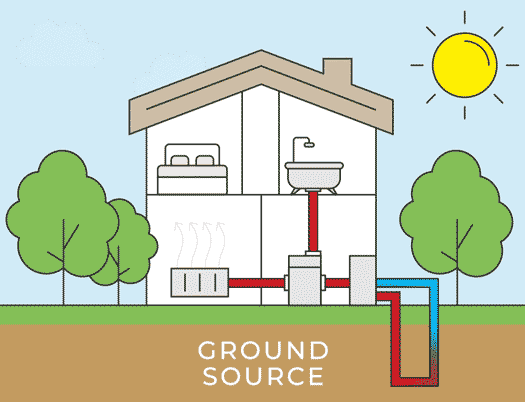
Air Source Heat Pump Installation Process
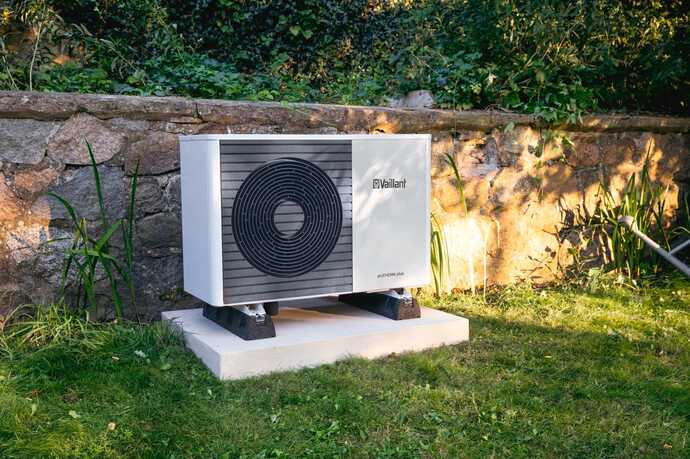
There are two types of air source heat pumps: air-to-air heat pumps and air-to-water heat pumps. The initial installation process for both systems remains the same. The outdoor unit is installed outside the home on a concrete base, ideally in an area with good airflow. Let’s delve into the details of each step in the air source heat pump installation process.
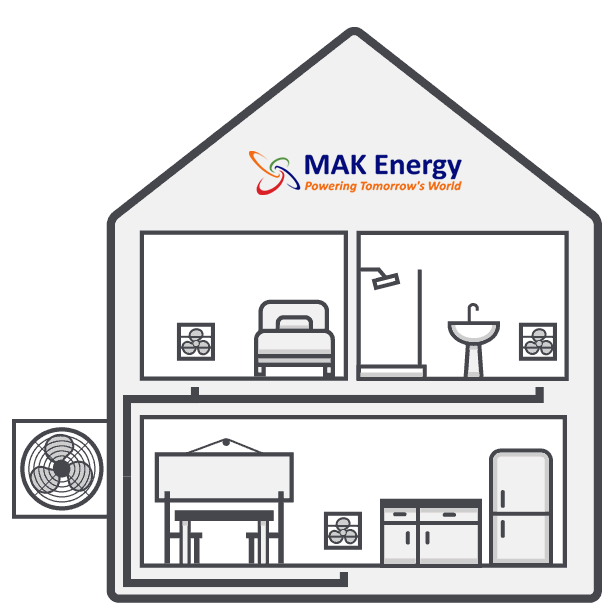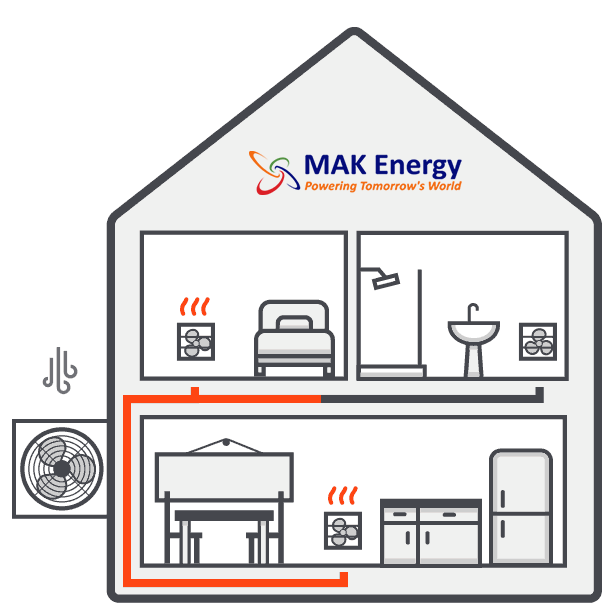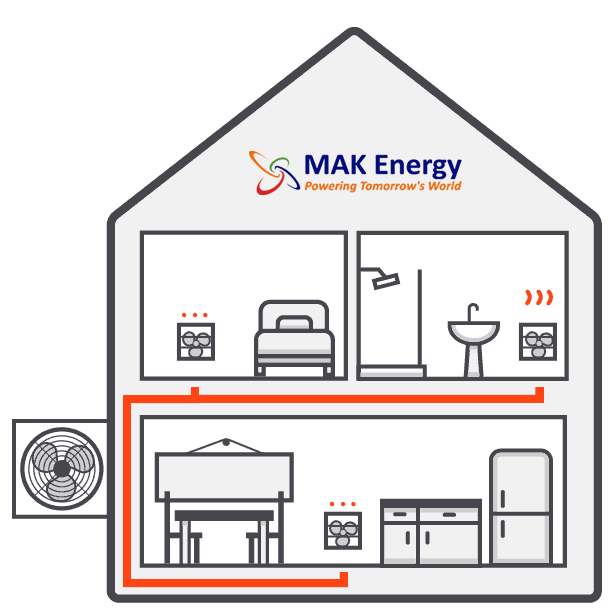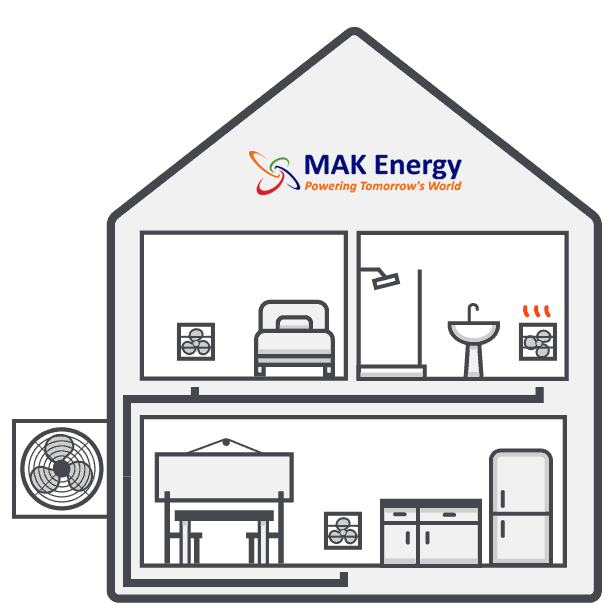
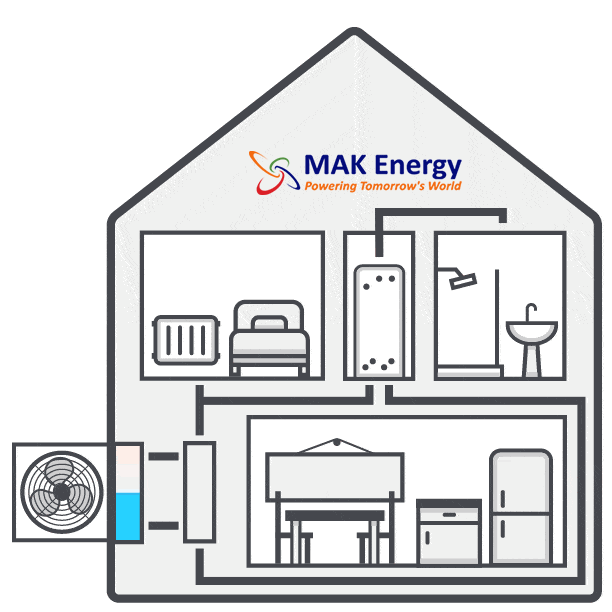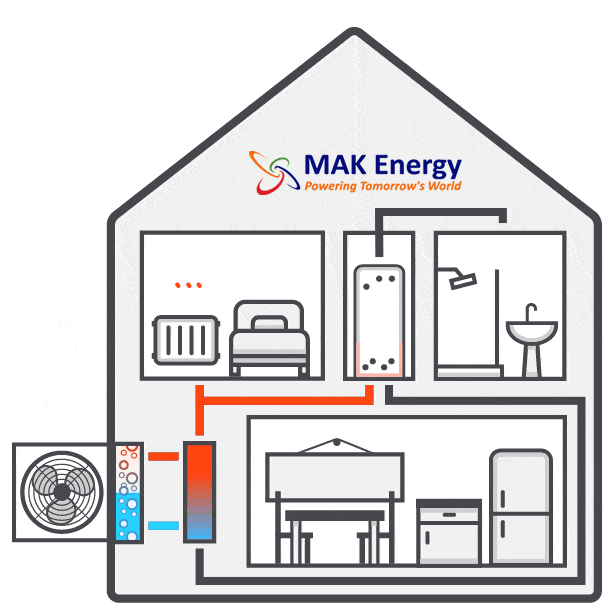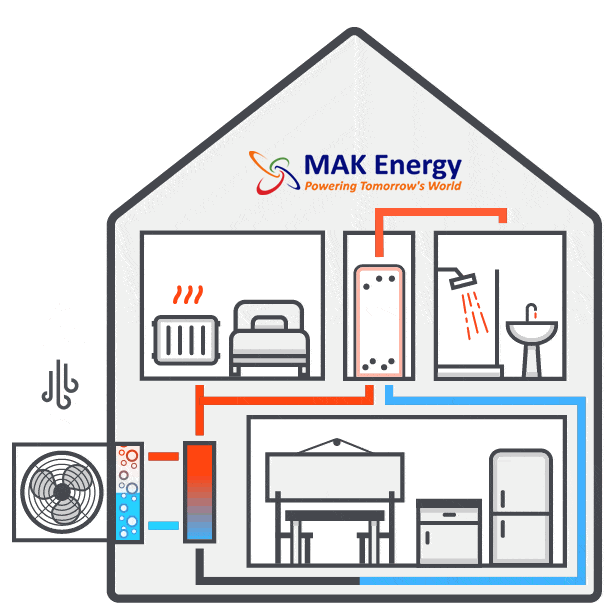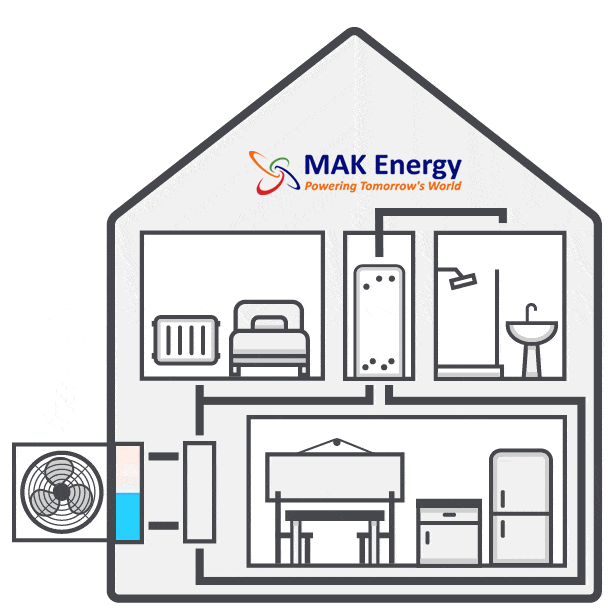
Pre-Installation Work- Inspection and Preparation
The first step involves site inspection and suitability assessment for air source heat pump installation. You would need to request the air source heat pump installer to send an engineer for a pre-installation inspection to determine the optimal size of the air source heat pump required for your needs. Once the inspection is completed, the air source heat pump installer company will provide a report detailing the sketched property layout.
The initial inspection is often performed by the air source heat pump installer companies at no cost, but some companies may charge a couple of hundred pounds. However, this fee is typically waived if you choose to proceed with the heat pump installation through the same company.

During the inspection, the engineer will measure the appropriate size of the air source heat system for your property, recommend the most suitable type for your home, determine the number of rooms requiring heating, assess insulation levels, and evaluate the dimensions of your current heating system. After completing the inspection, the engineer might suggest improving your home’s insulation for better efficiency, or they may recommend adding larger radiators or underfloor heating.
Installation of Outdoor Unit
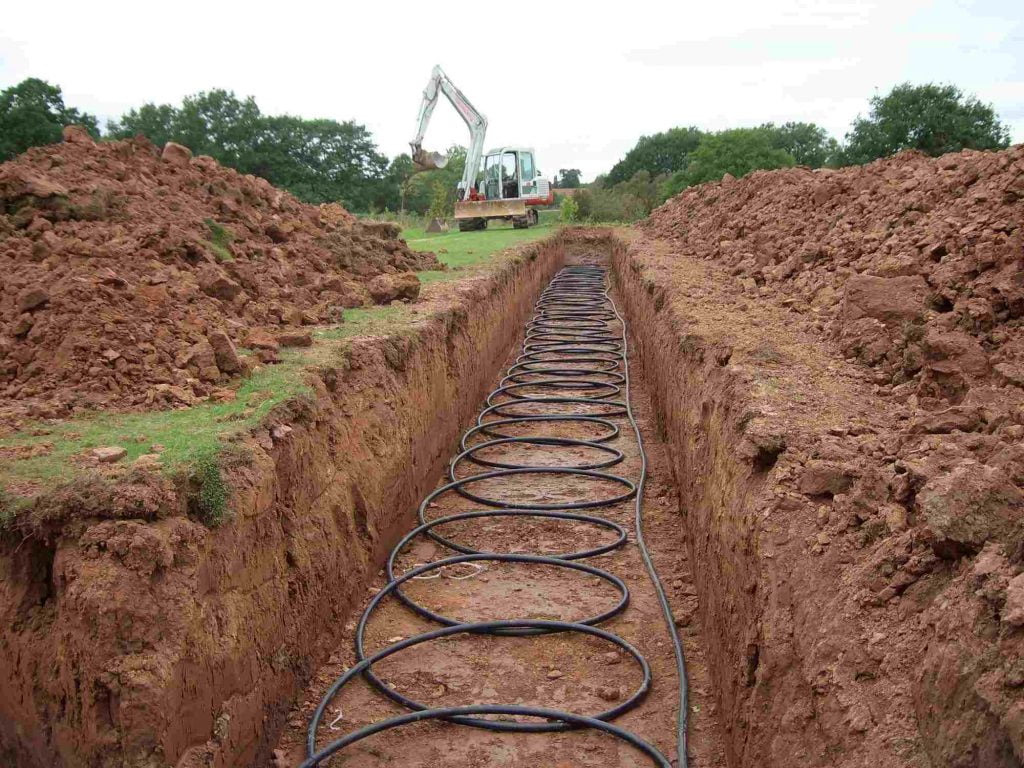
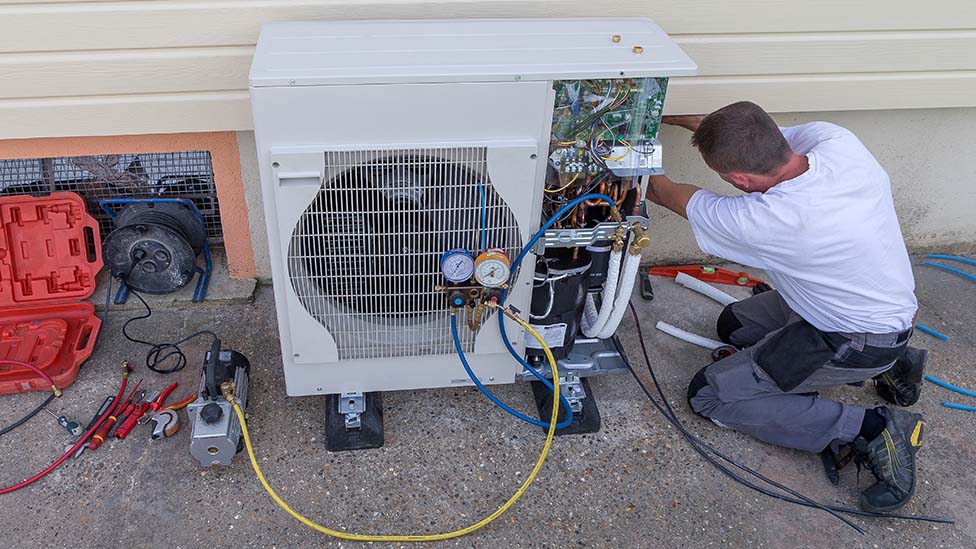
The outdoor unit is then installed outside your home, positioned next to an external wall. Because the heat pump requires unobstructed airflow, the installer will identify the most suitable location for the outdoor unit installation. It will either be placed on a concrete flat base or attached to the wall using brackets. The outdoor unit is installed in a way that ensures its stability in all weather conditions.

Installation of Indoor Unit
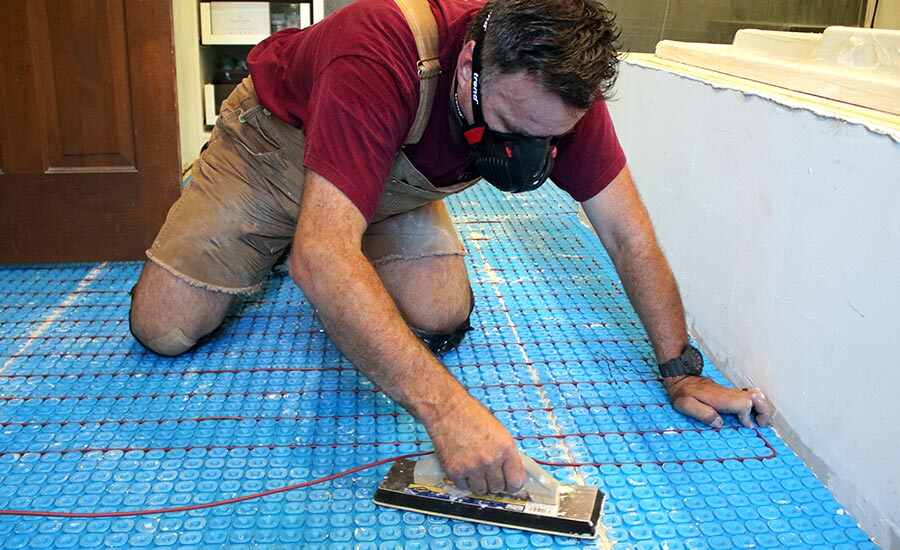
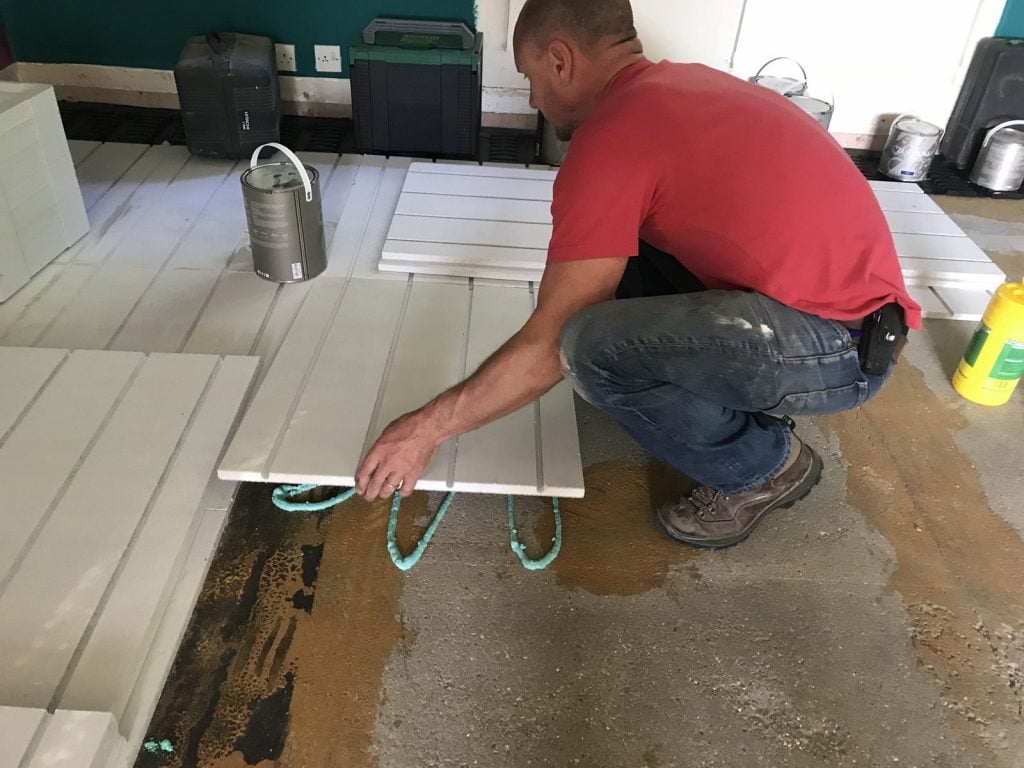
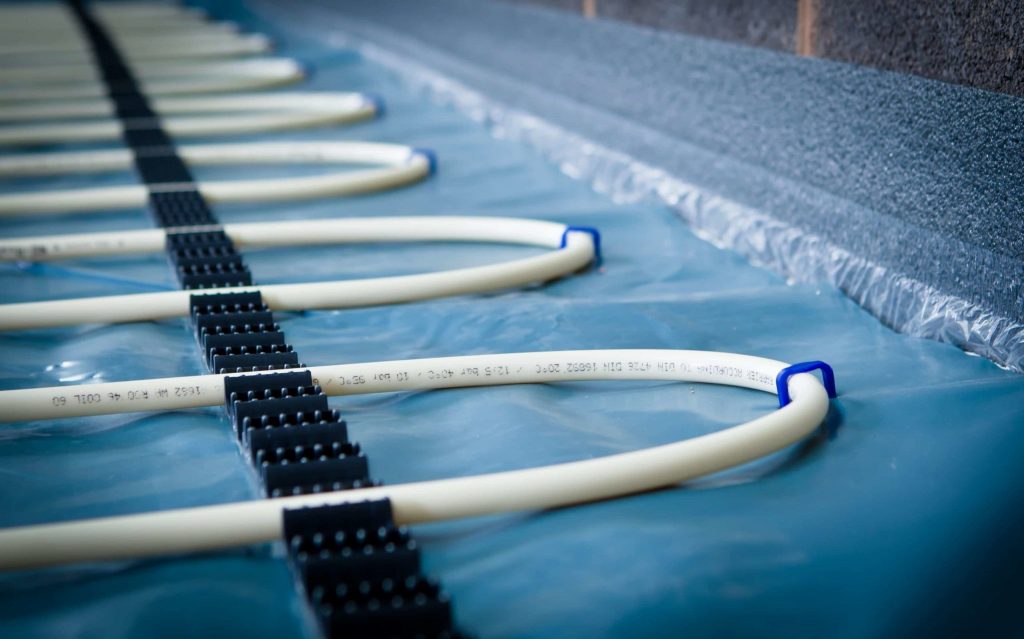
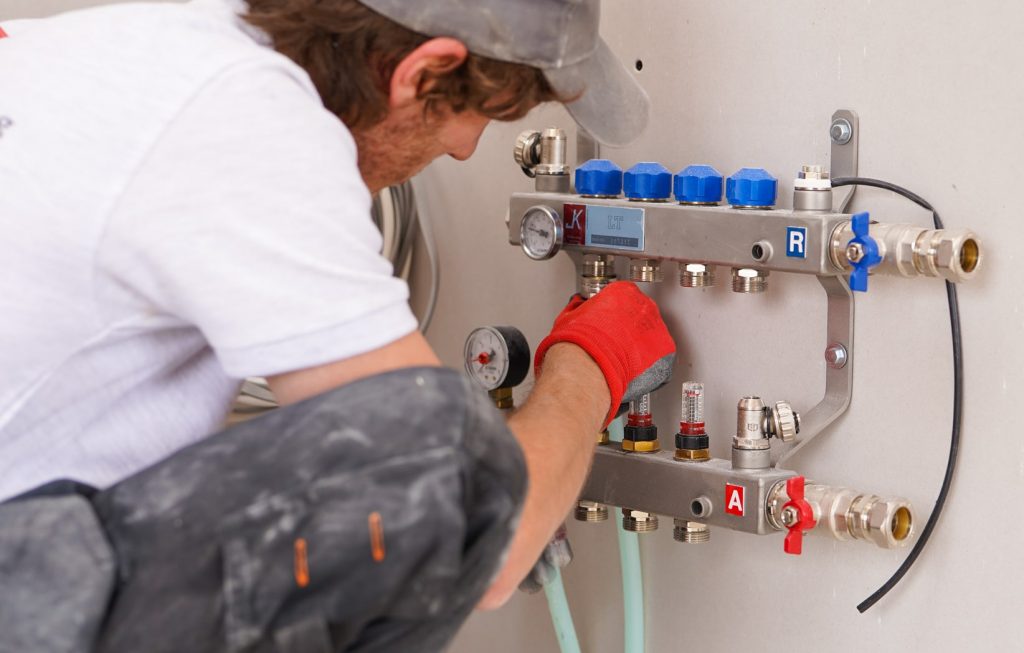
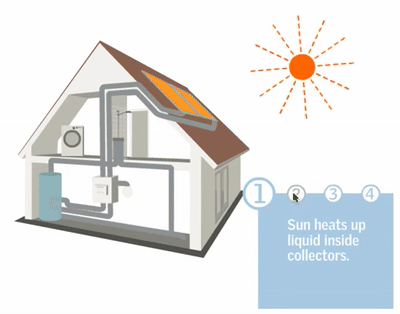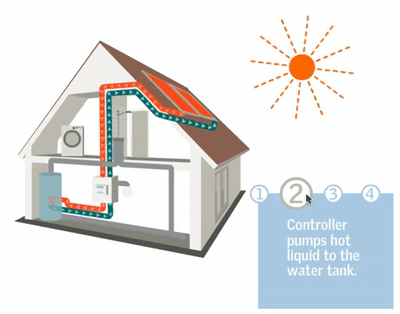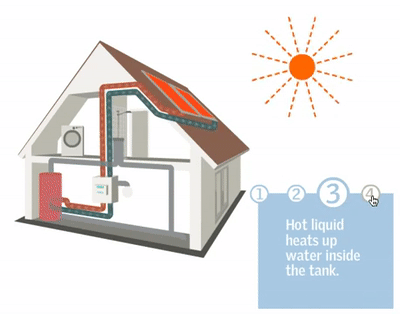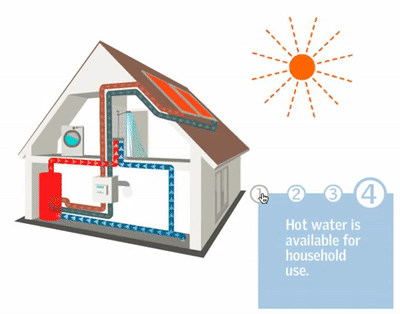
After installing an air source heat pump outdoor unit, the installer will move inside for the installation of the indoor unit. The indoor unit is installed and connected to either radiators, hot water pipes, or underfloor heating. A professional air source heat pump installer will recommend the appropriate size for your home; for instance, the average UK home with three bedrooms typically requires a 200-liter hot water cylinder.
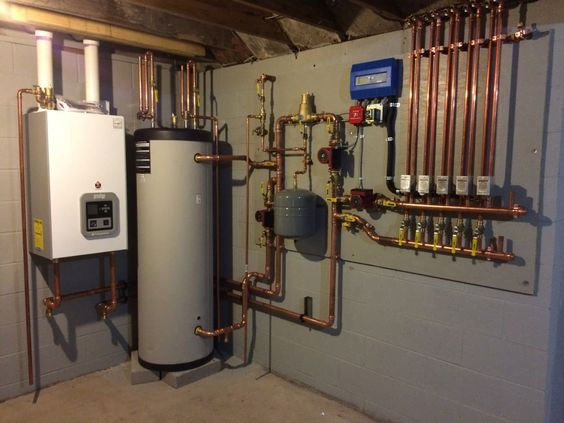

Connecting the Units
Now comes the stage of interconnecting all the components. Using wires, a condensate drain hose, and a refrigerant hose, the installer will establish a connection between the internal hot water cylinder and the external heat pump. These connections are typically established by drilling a hole through the wall. Throughout this process, there might be a brief interruption in your old heating system, but this typically lasts only a matter of hours.

Post-Installation Work
The process doesn’t conclude once the system is installed; there are some finishing touches to ensure the air source heat pump operates efficiently. Following installation, you can inquire about air source heat pump maintenance. While it requires minimal upkeep, maintaining your system is essential for achieving higher efficiency and extending its lifespan. This may involve tasks such as cleaning the fan or checking the filter annually.
How Much Does an Air Source Heat Pump Installation Cost?
The air source heat pump installation cost, including labor, VAT, and installation charges, can range from £8500 to £18500. The installation cost varies based on factors like system size, type, and installation complexity. To receive an accurate quote for an air source heat pump, simply complete our quotation form. You will swiftly receive a free, no-obligation quotation, along with the added benefit of a complimentary online survey.
- The air-to-air source heat pump installation cost, including labor, VAT, and installation charges, can range from £8500 to £18500
- The air-to-water source heat pump installation cost, including labor, VAT, and installation charges, can range from £6,900 to £12,500
Can You DIY Air Source Heat Pump Installation?
Yes, an air source heat pump installation could be carried out by yourself, but only if you possess experience and expertise in every aspect of air source heat pump installation. However, it is strongly recommended to hire a professional installer to ensure optimal performance from your heat pump. Even a small mistake during DIY installation could result in costly repairs, potentially amounting to thousands of pounds.
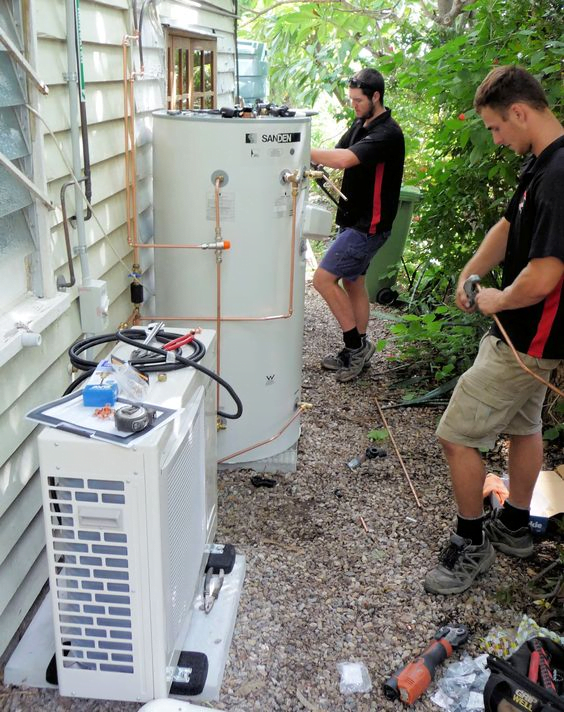

Connecting the units and handling the wiring requires a certified installer with specialized experience due to the complexity involved. To extend the lifespan of your air source heat pump and attain maximum efficiency, investing in a proper installation is highly advised.
How Long Does It take to Install an Air Source Heat Pump?
An air source heat pump installation usually takes between 2 to 5 days, depending on the complexity and size of the system. In most cases, the heat pump installation doesn’t require planning permission, which can expedite the process even further. However, it’s essential to confirm the planning permission requirements before proceeding with the installation.

How to Choose the Right Heat Pump Installer?
A correct choice of installer not only ensures a smooth installation process but also enhances the efficiency and lifespan of the heat pump. Before hiring a heat pump installer in the UK, ensure that the company is MCS-Certified and has received positive customer reviews. The best approach to selecting the optimal heat pump installer involves obtaining quotations from multiple installers, and subsequently comparing their services, pricing, and history related to heat pump installations.
Choose MAK Energy as your heat pump installer, as we possess MCS-Certification, boast positive customer reviews, and hold extensive experience in successfully installing an air source heat pump systems across the UK.

Summary
An air source heating system is highly efficient in providing heat, capable of delivering three times more heat energy than the electrical energy it consumes. Its installation process is somewhat lengthier and can take 2-5 days, depending on the complexity of the system. The process begins with an inspection and concludes with finishing touches, which involve checking the efficiency and functionality of the entire system.
Comparatively, an air source heating system is relatively expensive compared to other heating systems. The air source heat pump installation cost ranges between £800 and £1800, depending on the system’s size and heating requirements.